Simultaneous Grouping and Denoising via Sparse Convex Wavelet Clustering
Abstract: Clustering is a ubiquitous problem in data science and signal processing. In many applications where we observe noisy signals, it is common practice to first denoise the data, perhaps using wavelet denoising, and then to apply a clustering algorithm. In this paper, we develop a sparse convex wavelet clustering approach that simultaneously denoises and discovers groups. Our approach utilizes convex fusion penalties to achieve agglomeration and group-sparse penalties to denoise through sparsity in the wavelet domain. In contrast to common practice which denoises then clusters, our method is a unified, convex approach that performs both simultaneously. Our method yields denoised (wavelet-sparse) cluster centroids that both improve interpretability and data compression. We demonstrate our method on synthetic examples and in an application to NMR spectroscopy.
Publisher DOI: 10.1109/DSLW51110.2021.9523413
Working Copy: ArXiv 2012.04762
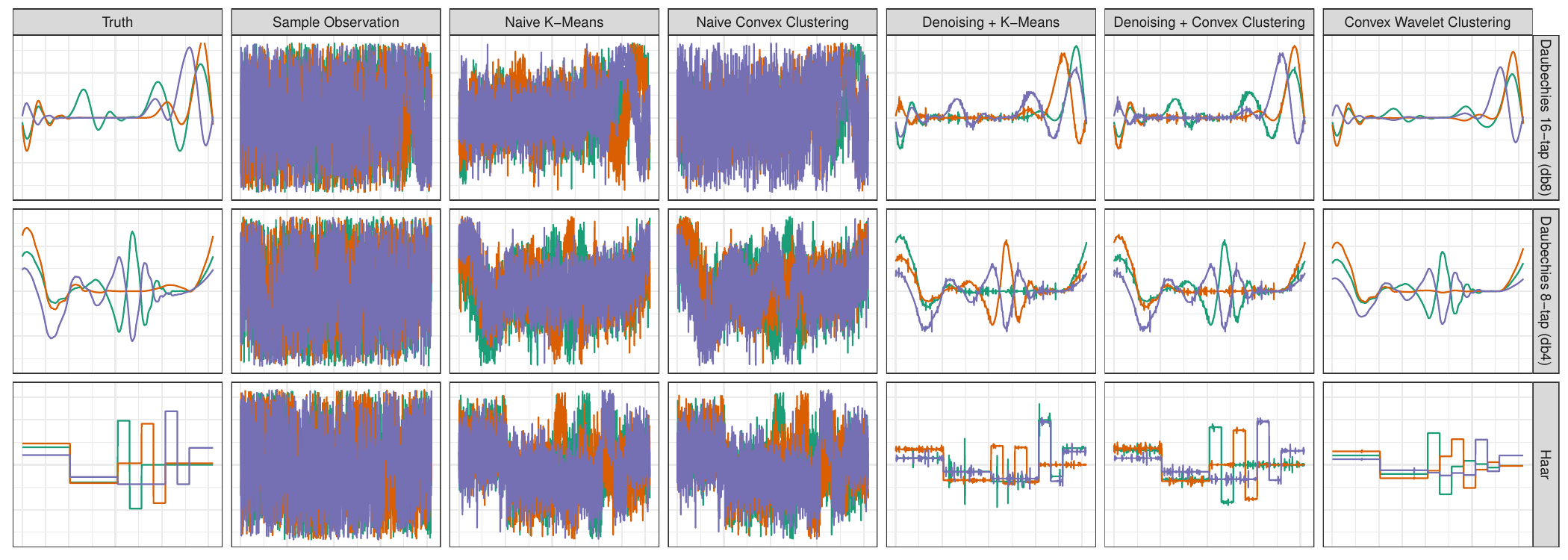
Summary: We consider the problem of clustering highly noisy signals. The dual nature of this problem gives rise to a puzzle: if we denoise the individual signals and then cluster, the resulting cluster centroids will be noisy, but if we cluster and then denoise, our clustering accuracy will be sub-par. We instead propose to simultaneous denoise and to cluster by combining wavelet soft-thresholding with convex clustering. The resulting approach identifies clusters which are denoised (wavelet sparse), while retaining the excellent statistical performance of convex clustering:
 Our approach be expressed as the following convex optimization problem:
Our approach be expressed as the following convex optimization problem:
[ | - |F^2 + {}^n w_{ij} |{i} - {j}|2 + {j = 1}^T i |{j}|_2]
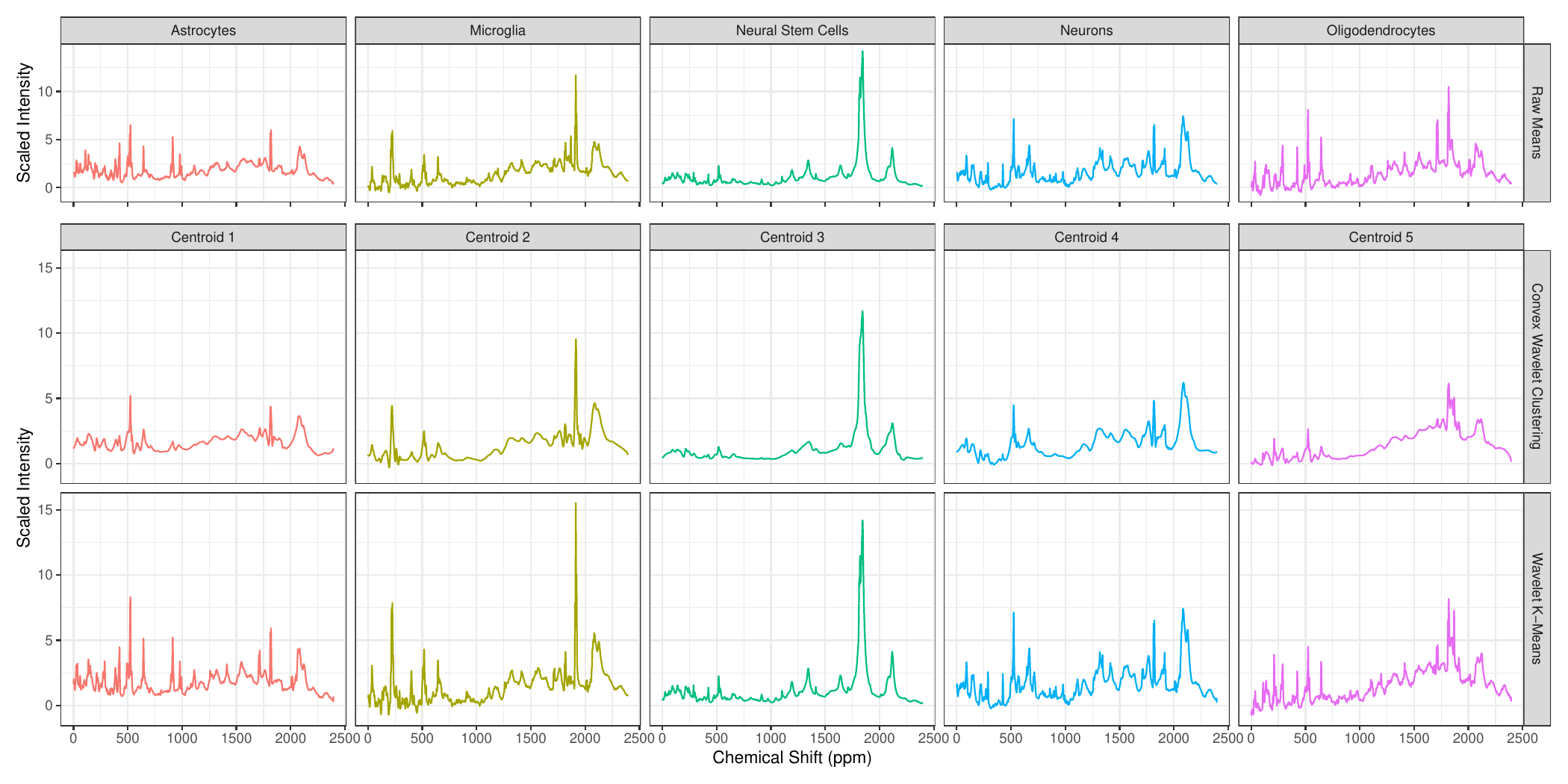
If \(\Psi\) represents a full-rank wavelet basis, this reduces to the sparse convex clustering problem on the wavelet coefficients, for which we provide a new and efficient algorithm. We apply this approach to a cell-subtyping problem in which (noisy) NMR spectra are sampled from individual brain cells. Our approach is able to identify the different cell lines most accurately and to identify key NMR peaks identifying each cell type.
Citation:
@INPROCEEDINGS{Weylandt:2021-ConvexWaveletClustering,
AUTHOR="Michael Weylandt and T. Mitchell Roddenberry and Genevera I. Allen",
TITLE="Simultaneous Grouping and Denoising via Sparse Convex Wavelet Clustering",
DOI="10.1109/DSLW51110.2021.9523413"
PAGES={1-8},
CROSSREF="DSLW:2021"
}
@PROCEEDINGS{DSLW:2021,
BOOKTITLE="DSLW 2021: Proceedings of the IEEE Data Science and Learning Workshop 2021",
YEAR=2021,
LOCATION="Toronto, Canada"
EDITOR="Stark Draper and Z. Jane Wang"
}